Setting up R Packages
Plot Theme
Show the Code
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/74491138/ggplot-custom-fonts-not-working-in-quarto
# Chunk options
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
fig.width = 7,
fig.asp = 0.618, # Golden Ratio
# out.width = "80%",
fig.align = "center"
)
### Ggplot Theme
### https://rpubs.com/mclaire19/ggplot2-custom-themes
theme_custom <- function() {
font <- "Roboto Condensed" # assign font family up front
theme_classic(base_size = 14) %+replace% # replace elements we want to change
theme(
panel.grid.minor = element_blank(), # strip minor gridlines
text = element_text(family = font),
# text elements
plot.title = element_text( # title
family = font, # set font family
size = 20, # set font size
face = "bold", # bold typeface
hjust = 0, # left align
# vjust = 2 #raise slightly
margin = margin(0, 0, 10, 0)
),
plot.subtitle = element_text( # subtitle
family = font, # font family
size = 14, # font size
hjust = 0,
margin = margin(2, 0, 5, 0)
),
plot.caption = element_text( # caption
family = font, # font family
size = 8, # font size
hjust = 1
), # right align
axis.title = element_text( # axis titles
family = font, # font family
size = 10 # font size
),
axis.text = element_text( # axis text
family = font, # axis family
size = 8
) # font size
)
}
# Set graph theme
theme_set(new = theme_custom())
#Introduction
The extent of Antarctic Sea Ice over time is monitored by the National Snow and Ice Data Center https://nsidc.org/.
Read the Data
The data is an excel sheet. Inspect it first in Excel and decide which sheet you need, and which part of the data you need. There are multiple sheets! Then use readxl::read_xlsx(..) to read it into R. NOTE: The sheet that contains our data of interest is titled “SH-Daily-Extent”.
Inspect the Data
...1 <chr> | ...2 <dbl> | 1978 <dbl> | 1979 <dbl> | 1980 <dbl> | 1981 <dbl> | 1982 <dbl> | 1983 <dbl> | 1984 <dbl> | 1985 <dbl> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 1 | NA | NA | 5.967 | 6.323 | NA | 6.508 | NA | NA | |
| NA | 2 | NA | 6.945 | NA | NA | 7.039 | NA | 6.944 | 6.527 | |
| NA | 3 | NA | NA | 5.674 | 5.791 | NA | 6.170 | NA | NA | |
| NA | 4 | NA | 6.838 | NA | NA | 6.689 | NA | 6.653 | 6.061 | |
| NA | 5 | NA | NA | 5.584 | 5.351 | NA | 5.869 | NA | NA | |
| NA | 6 | NA | 6.638 | NA | NA | 6.393 | NA | 6.296 | 5.665 | |
| NA | 7 | NA | NA | 5.329 | 5.191 | NA | 5.660 | NA | NA | |
| NA | 8 | NA | 6.270 | NA | NA | 6.084 | NA | 5.935 | 5.310 | |
| NA | 9 | NA | NA | 5.000 | 4.775 | NA | 5.305 | NA | NA | |
| NA | 10 | NA | 6.138 | NA | NA | 5.862 | NA | 5.629 | 4.934 |
Appreciate the structure of this data. You may even want to open it in Excel for a closer look. List any imperfections in your Data Dictionary. Why do these matter now? Why might they not have mattered earlier, up to now?
Data Dictionary
Write in.
Write in.
Write in.
Analyse/Transform the Data
Try to figure what may be needed, based on the imperfections noted above, what you may attempt to clean the data. Refer to your “list of imperfections” in the data.
Then look at the code below and execute line by line to get an idea.
```{r}
#| label: data-preprocessing
#
# Write in your code here
# to prepare this data as shown below
# to generate the plot that follows
```Show the Code
ice %>%
# Select columns
# Rename some while selecting !!
select("month" = ...1, "day" = ...2, c(4:49)) %>%
# Fill the month column! Yes!!
tidyr::fill(month) %>%
# Make Wide Data into Long
pivot_longer(
cols = -c(month, day),
names_to = "series",
values_to = "values"
) %>%
# Regular Munging
mutate(
series = as.integer(series),
month = factor(month,
levels = month.name,
labels = month.name,
ordered = TRUE
),
# Note munging for date!!
# Using the lubridate package, part of tidyverse
date = lubridate::make_date(
year = series,
month = month,
day = day
)
) -> ice_prepared
ice_preparedmonth <ord> | day <dbl> | series <int> | values <dbl> | date <date> |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 1 | 1979 | NA | 1979-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1980 | 5.967 | 1980-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1981 | 6.323 | 1981-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1982 | NA | 1982-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1983 | 6.508 | 1983-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1984 | NA | 1984-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1985 | NA | 1985-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1986 | 7.718 | 1986-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1987 | NA | 1987-01-01 |
| January | 1 | 1988 | NA | 1988-01-01 |
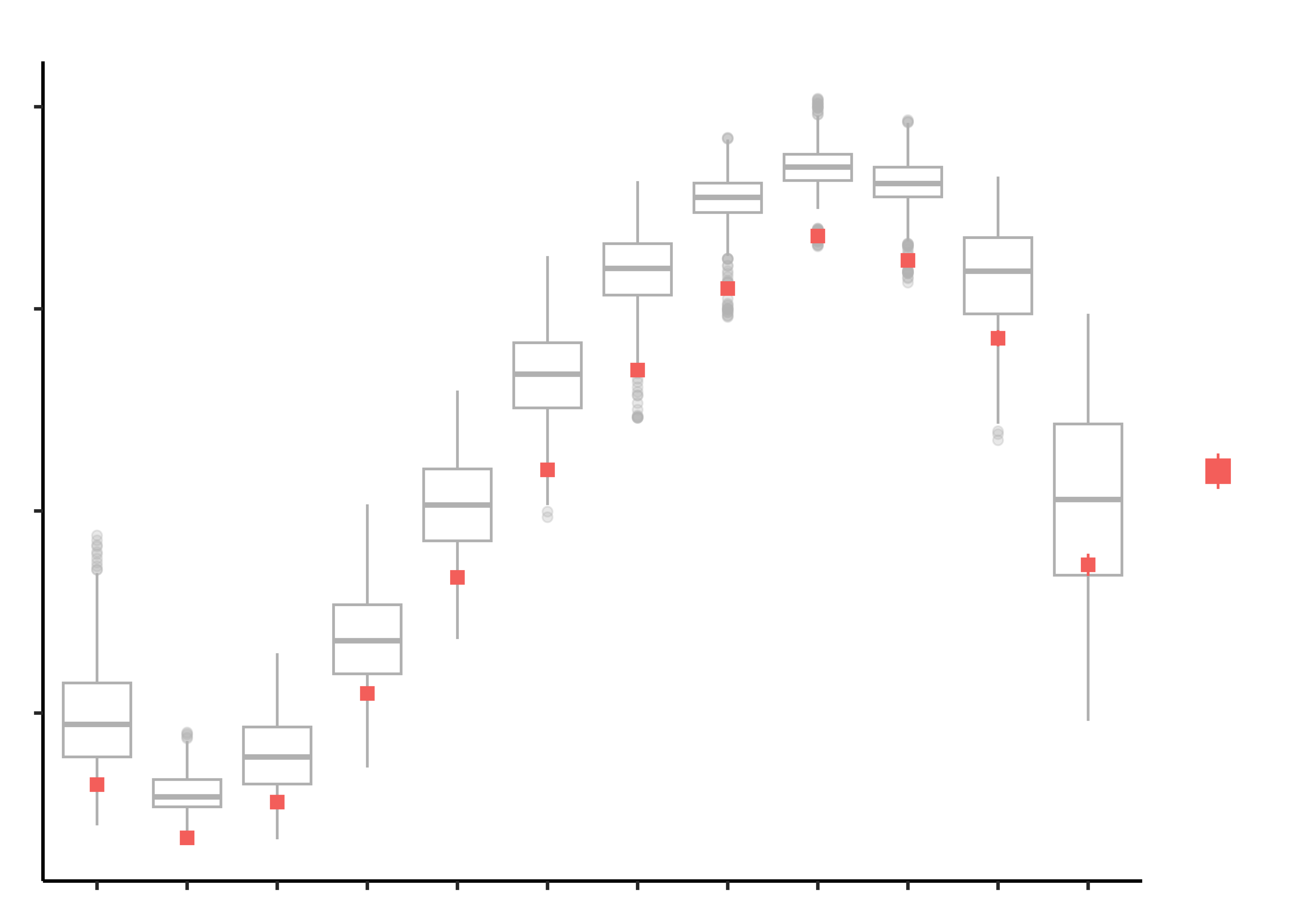
Research Question
Write in! Look first at the graph!
Plot the Data
Tasks and Discussion
- Complete the Data Dictionary.
- Select and Transform the variables as shown.
- Create the graphs shown and discuss the following questions:
- Identify the type of charts
- Identify the variables used for various geometrical aspects (x, y, fill…). Name the variables appropriately.
- What research activity might have been carried out to obtain the data graphed here? Provide some details.
- What might have been the Hypothesis/Research Question to which the response was Chart?
- What might the red points represent?
- What is perhaps a befuddling aspect of this graph until you…Ohhh!!!!!!
- Draw a sketch of a similar chart for ice extents in the Arctic.