library(tidyverse)
library(sf)
library(tmap)
library(tmaptools)
# install.packages("remotes")
# remotes::install_github("r-tmap/tmap.mapgl")
library(tmap.mapgl) # Free mapgl maps
library(osmdata)
library(rnaturalearth)
## Interactive Maps
library(leaflet)
library(leaflet.providers)
library(leaflet.extras)
##
library(tidyplots) # Easily Produced Publication-Ready Plots
library(tinyplot) # Plots with Base R
library(tinytable) # Elegant Tables for our data
Maps, Cartograms, and Choropleths
Slides and Tutorials
| Spatial Data | Static Maps | Interactive Maps with Leaflet | Interactive Maps with Mapview |
Data |
Maps |
with leaflet |
with mapview |
“If we were to wake up some morning and find that everyone was the same race, creed, and color, we would find some other cause for prejudice by noon.”
— George D. Aiken, US senator (20 Aug 1892-1984)
Plot Fonts and Theme
Show the Code
library(systemfonts)
library(showtext)
## Clean the slate
systemfonts::clear_local_fonts()
systemfonts::clear_registry()
##
showtext_opts(dpi = 96) # set DPI for showtext
sysfonts::font_add(
family = "Alegreya",
regular = "../../../../../../fonts/Alegreya-Regular.ttf",
bold = "../../../../../../fonts/Alegreya-Bold.ttf",
italic = "../../../../../../fonts/Alegreya-Italic.ttf",
bolditalic = "../../../../../../fonts/Alegreya-BoldItalic.ttf"
)Error in check_font_path(bold, "bold"): font file not found for 'bold' typeShow the Code
sysfonts::font_add(
family = "Roboto Condensed",
regular = "../../../../../../fonts/RobotoCondensed-Regular.ttf",
bold = "../../../../../../fonts/RobotoCondensed-Bold.ttf",
italic = "../../../../../../fonts/RobotoCondensed-Italic.ttf",
bolditalic = "../../../../../../fonts/RobotoCondensed-BoldItalic.ttf"
)
showtext_auto(enable = TRUE) # enable showtext
##
theme_custom <- function() {
font <- "Alegreya" # assign font family up front
theme_classic(base_size = 14, base_family = font) %+replace% # replace elements we want to change
theme(
text = element_text(family = font), # set base font family
# text elements
plot.title = element_text( # title
family = font, # set font family
size = 24, # set font size
face = "bold", # bold typeface
hjust = 0, # left align
margin = margin(t = 5, r = 0, b = 5, l = 0)
), # margin
plot.title.position = "plot",
plot.subtitle = element_text( # subtitle
family = font, # font family
size = 14, # font size
hjust = 0, # left align
margin = margin(t = 5, r = 0, b = 10, l = 0)
), # margin
plot.caption = element_text( # caption
family = font, # font family
size = 9, # font size
hjust = 1
), # right align
plot.caption.position = "plot", # right align
axis.title = element_text( # axis titles
family = "Roboto Condensed", # font family
size = 12
), # font size
axis.text = element_text( # axis text
family = "Roboto Condensed", # font family
size = 9
), # font size
axis.text.x = element_text( # margin for axis text
margin = margin(5, b = 10)
)
# since the legend often requires manual tweaking
# based on plot content, don't define it here
)
}
## Use available fonts in ggplot text geoms too!
update_geom_defaults(geom = "text", new = list(
family = "Roboto Condensed",
face = "plain",
size = 3.5,
color = "#2b2b2b"
))
## Set the theme
theme_set(new = theme_custom())What graphs will we see today?
| Variable #1 | Variable #2 | Chart Names | Chart Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quant | Qual | Choropleth and Symbols Maps, Cartograms |
|
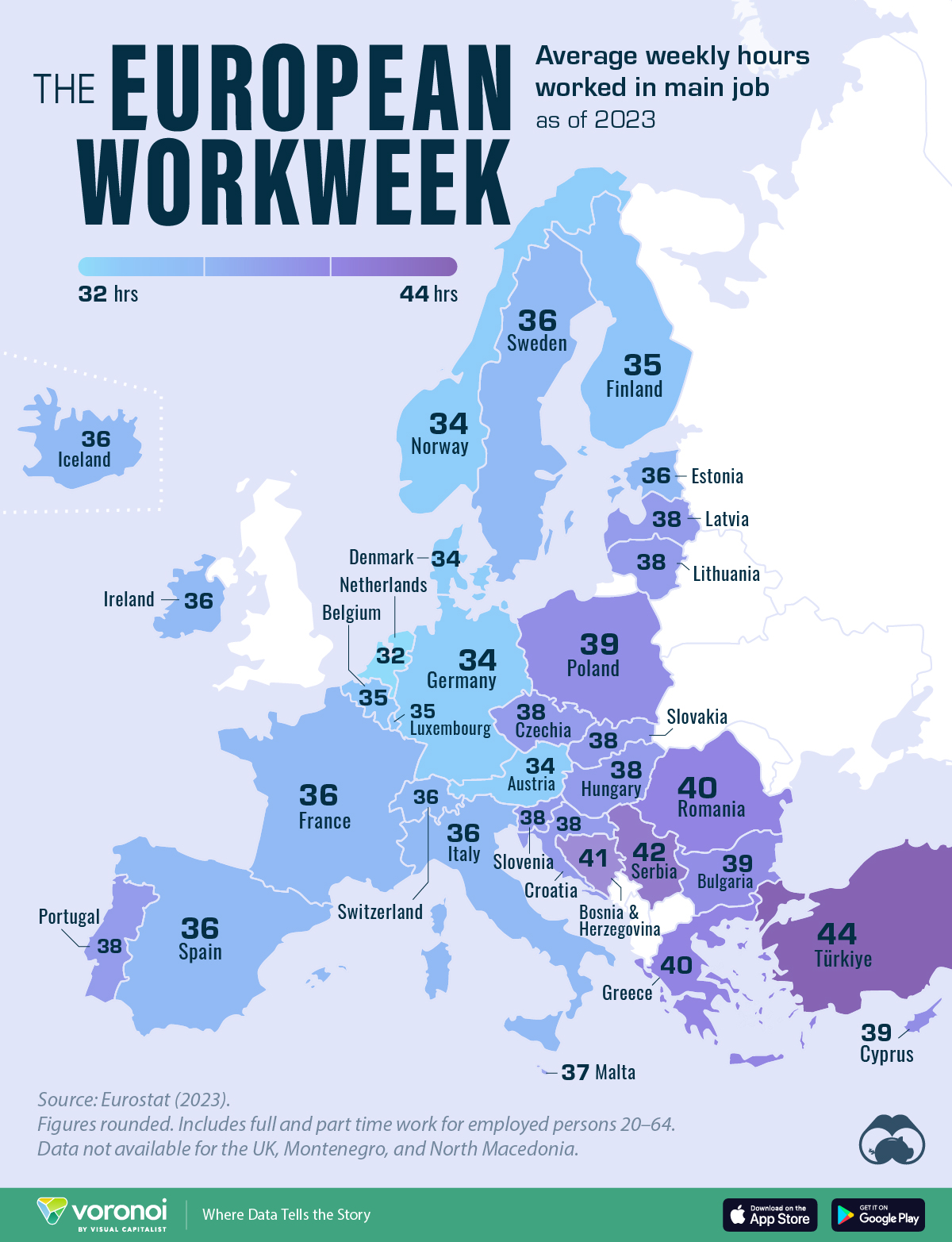
In Figure 1 (a), we have a choropleth map. What does choropleth1 mean? And what kind of information could this map represent? The idea is to colour a specific area of the map, a district or state, based on a Quant or a Qual variable.
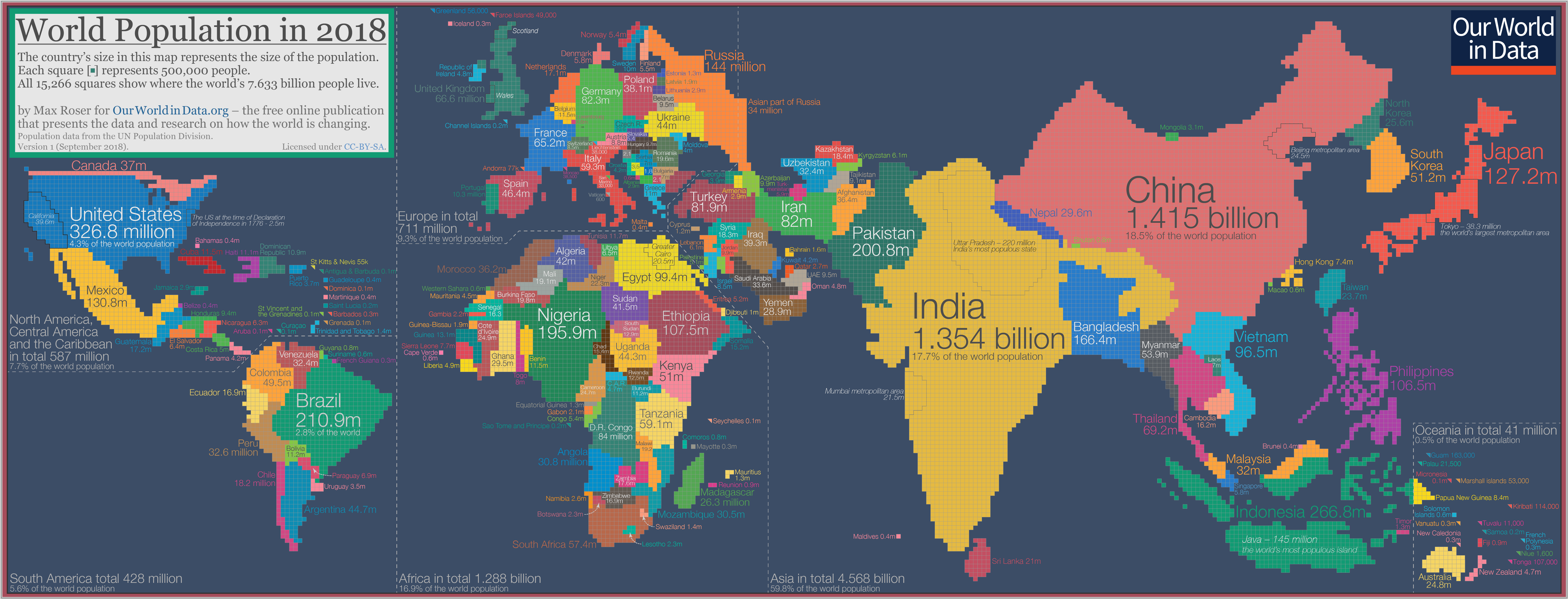
The Figure 1 (b) deliberately distorts and scales portions of the map in proportion to a Quant variable, in this case, population in 2018.
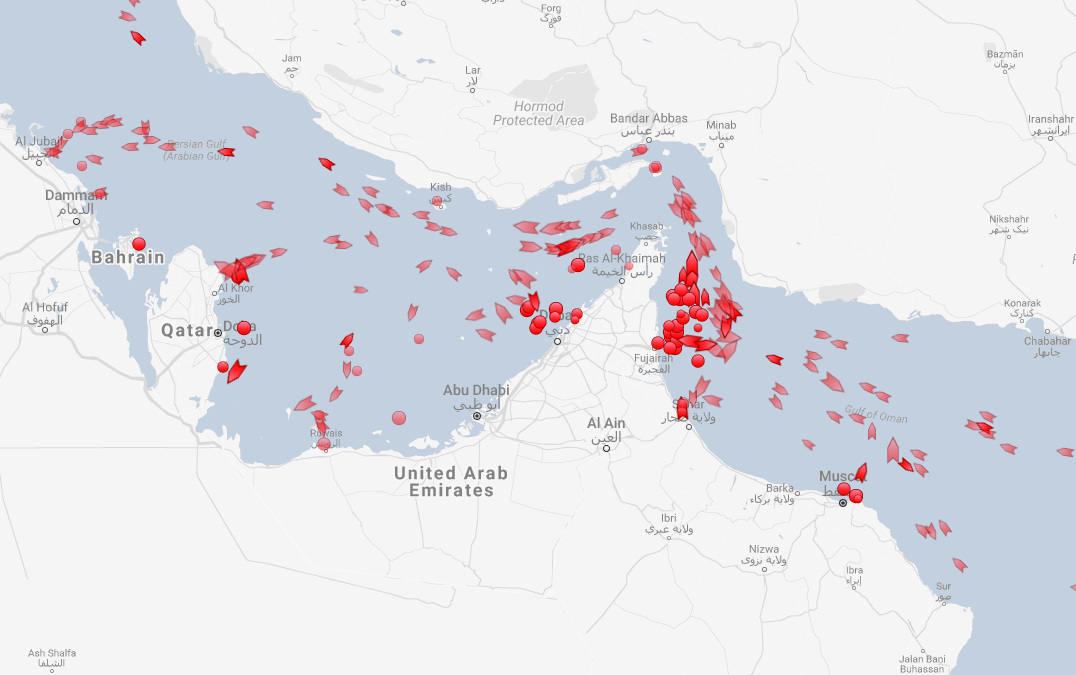
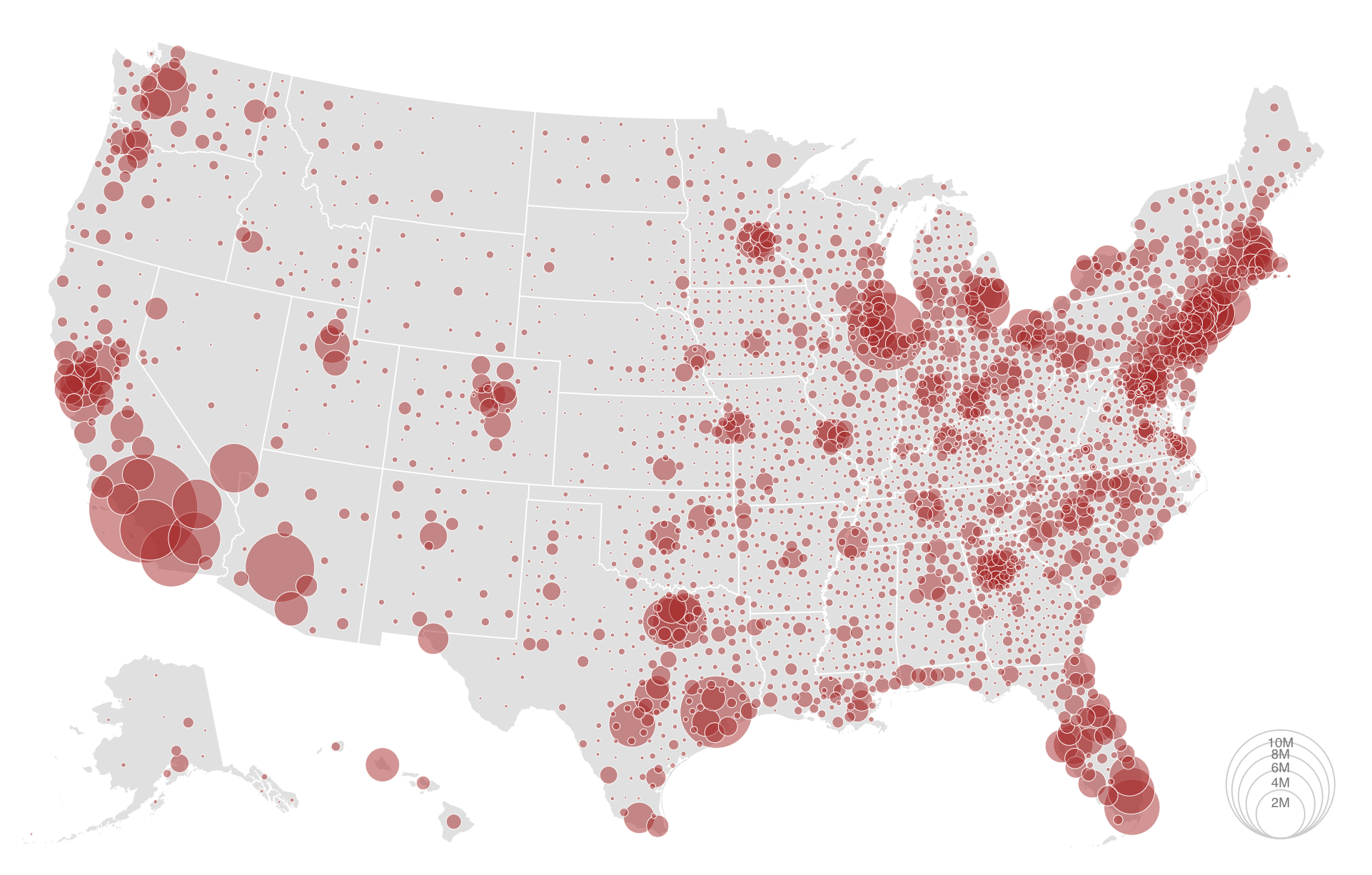
In Figure 2 (a) and Figure 2 (b), symbols are used to indicate either the location/presence of an item of interest, or a quantity by scaling their size in proportion to a Quant variable
First; let us watch a short, noisy video on maps:
Let us first understand the idea of a Geographical Information System, GIS:
We will first understand the structure of spatial data and where to find it. For now, we will deal with vector spatial data; the discussion on raster data will be dealt with in another future module.
We will get hands-on with making maps, both static and interactive.
What information could this map below represent?
Let us now look at the slides. Then we will understand how the R packages sf, tmap work to create maps, using data downloadable into R using osmdata and . We will also make interactive maps with osmplotrleaflet and mapview; tmap is also capable of creating interactive maps.
- Head off to movebank.org. Look at a few species of interest and choose one.
- Download the data ( ESRI Shapefile). Note: You will get a .zip file with a good many files in it. Save all of them, but read only the
.shpfile into R. - Import that into R using
sf_read() - See how you can plot locations, tracks and colour by species….based on the data you download.
- For tutorial info: https://movebankworkshopraleighnc.netlify.app/
Here is a UFO Sighting dataset, containing location and text descriptions. https://github.com/planetsig/ufo-reports/blob/master/csv-data/ufo-scrubbed-geocoded-time-standardized.csv
Head off to Kaggle and search for Geographical Sales related data. Make both static and interactive maps with this data. Justify your decisions for type of map.
- Hadley Wickham, Danielle Navarro and Thomas Lin Pedersen. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, https://ggplot2-book.org/maps.html
- Martijn Tennekes and Jakub Nowosad (2025). Elegant and informative maps with tmap. https://tmap.geocompx.org
- Robin Lovelace, Jakub Nowosad, Jannes Muenchow. Geocomputation with R. https://r.geocompx.org/
- Emine Fidan. Guide to Creating Interactive Maps in R, https://bookdown.org/eneminef/DRR_Bookdown/
- Nikita Voevodin. R, Not the Best Practices, https://bookdown.org/voevodin_nv/R_Not_the_Best_Practices/maps.html
- Want to make a cute logo-like map? Try https://prettymapp.streamlit.app
- Free Map Tile services. https://alexurquhart.github.io/free-tiles/
Footnotes
Etymology. From Ancient Greek χώρα (khṓra, “location”) + πλῆθος (plêthos, “a great number”) + English map. First proposed in 1938 by American geographer John Kirtland Wright to mean “quantity in area,” although maps of the type have been used since the early 19th century.↩︎
Citation
@online{2022,
author = {},
title = {\textless Iconify-Icon Icon=“gis:proj-Geo” Width=“1.2em”
Height=“1.2em”\textgreater\textless/Iconify-Icon\textgreater{}
{Space}},
date = {2022-08-15},
url = {https://av-quarto.netlify.app/content/courses/Analytics/Descriptive/Modules/90-Space/},
langid = {en},
abstract = {Geospatial Data and how to use it with intent}
}